GlobalData: The Netherlands is on track to carbon-neutral

As the country that is home to one of the most sustainable cities—and a responsible country overall, the Netherlands is on track to phase out the use of coal power by the year 2030, according to GlobalData. The country is expected to reduce its coal-powered energy capacity to 3.18GW in 2025 before the complete elimination of the source.
Reliable and renewable energy sources
The leading data and analytics company highlighted this information in a report, which shows the effects of the Dutch government’s strategy for decarbonisation, as it imposes taxation on coal resources.
‘The Dutch Government’s ban on coal power generation follows its efforts to reduce greenhouse emissions by 49% by the end of 2030, as compared to 1990 levels’, says Rohit Ravetkar, Power Analyst at GlobalData. ‘The minimum carbon price floor announced by the government will discourage the use of fossil fuels for power generation. By heavily penalizing the greenhouse gas emitters, the carbon price floor will result in increased adoption of renewables. The carbon price floor was introduced in the UK in 2013 and resulted in significant growth for the renewable sector. A similar result is expected in the Netherlands’.
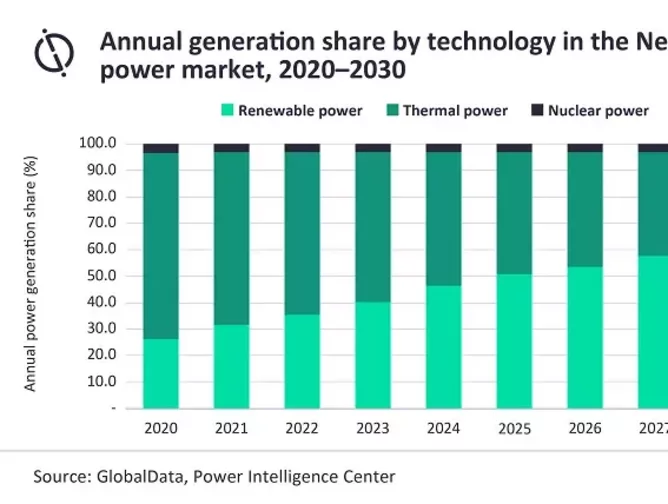
The latest report by GlobalData, Netherlands Power Market Outlook to 2030, shows the trends of the Dutch energy market as it watches the adoption of renewable energy increase. The data specifically shows that thermal energy generation will decrease in the coming years, which possessed 70.4% of the market share in 2020.
‘One requirement of the government’s ban is that coal-based power plants have to switch to [alternative] fuels such as sustainable biopower. Coal power plant owners are expected to spend a significant amount to retrofit their plants for switching to biopower. This will result in biopower capacity increasing from 1.21 GW in 2020 to 3.11 GW in 2030’, says Ravetkar.
He also adds, ‘in the last decade, the Dutch Government has encouraged power utilities to build coal power plants in the country. A few of the coal-fired plants were commissioned in 2015 with utilities spending more than $3bn for the construction of these plants. Now, utilities are unhappy with the compensation offered by the Dutch Government for closing down their coal power plants as it will massively affect their profits’.
The Dutch government has also made plans to phase out the use of nuclear power, three years after the deadline for decarbonisation. The country currently has one nuclear power reactor, with a power capacity of 482MW, owned by Pzem Energy BV and RWE AG, which is expected to be decommissioned by 2033.
Ravetkar says, ‘Rapidly phasing out coal and nuclear power – two major power generation sources – in such a short timeframe may reduce the reliability of the country’s electricity supply. The country needs to effectively balance its retiring power generation fleet with the proper base-load capacity to continue uninterrupted power generation in the future. It is highly likely that renewable power sources, especially solar PV and onshore wind, will fill the capacity void caused due to the phase-out of coal and nuclear power’.
For more energy insights, check out the latest issue of Energy Digital Magazine.






