Nanotubes' Unusual Electric Heat Property may Replace Batteries
Written By: John Shimkus
Scientists are forging new energy frontiers in the 21st century. From Quantum Computers to the Casimir Effect, technological breakthroughs are changing the way we understand the universe, and the biggest breakthroughs seem to be coming from the smallest of places. Take carbon nanotubes for example. These plasma-generated microscopic fibers are exhibiting some pretty unusual properties, but may hold secrets that can lead to efficient clean energy generation, possibly even replacing the traditional battery.
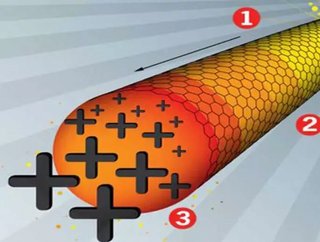
Scientists from MIT have been testing the different properties of nanotubes and one discovery in particular has the energy industry taking notice. In an experiment where nanotubes were coated in a reactive fuel and ignited at one end, studies reveal that the heat waves traveling through the tubes moved 10,000 times faster and reached higher temperatures than the ignition reaction typically exhibits without nanotubes. Even more curious is that the fast-moving thermal heat waves within the nanotubes picked up charged particles along the route, actually generating electricity!
SEE OTHER TOP STORIES IN THE WDM CONTENT NETWORK
Renewable Geothermal Energy Pumps Up Heat’s Power Potential
The Future of Batteries: A Distributed Approach to Energy Storage
Check out the latest issue of Energy Digital!
The researchers thus far have described the nanotube electric heat effect with the metaphor of ocean waves, which pick up debris and carry it along for the ride. Electrons and/or other charged particles are being picked up by the thermal wave within the nanotube and carried from one end to the other.
The researchers exploring this exciting new breakthrough believe that nanotubes may soon be used as batteries in various microscopic applications, specifically in the medical industry. However, larger-scale electricity generation may also be possible with nanotubes, although research has yet to investigate the practicality of such endeavors. Nanotubes may also serve as a new type of electrical wire that transfers both electricity and heat. The MIT research team even theorizes that different fuel coatings may produce alternating current (AC) power, in contrast to current energy storage systems that all produce direct current (DC) power. In any case, it looks like nanotubes may be the next big thing in the energy industry.
- Building Better Batteries Integral to Future EV SuccessSustainability
- Meet Dyson’s Battery Technology Expert New CEO Hanno KirnerRenewable Energy
- Cleaner future on horizon with cell manufacturing facilitySustainability
- ExxonMobil to power the future of EVs with Arkansas lithiumSustainability






